Top 4 Applications of 3D Scanning [Explained in Detail]
Posted by Peyton Michaels on 20th Nov 2024
In an era of rapid advancements, 3D scanning technology is revolutionizing how we approach design, manufacturing, healthcare, construction, and heritage preservation.
By capturing detailed, high-resolution data, 3D scanning helps you work faster, more accurately, and confidently in numerous fields.
In this article, we’ll explore the top four applications of 3D scanning, diving into how this technology is actively shaping industries and improving outcomes across diverse scenarios.
Precision Manufacturing & Quality Control
When it comes to manufacturing, 3D scanning offers unmatched accuracy. This technology enables you to create precise models for every stage of the production process, from initial prototyping to final quality checks.
With 3D scanning, you can capture intricate details down to the micron level, ensuring that each part matches the specifications.
In quality control, 3D scanning plays a key role in identifying even the smallest defects. For example, in the automotive and aerospace industries, where every component must meet strict safety and performance standards, 3D scanning can spot minute inconsistencies that traditional methods might miss.
By scanning parts throughout the production line, you can address potential issues early, reducing waste and rework while ensuring that every piece meets the desired quality.
Real-World Applications
Consider automotive manufacturing, where precision is critical. With 3D scanning, you can quickly inspect each part for alignment, size, and quality, ensuring that every component fits perfectly and functions as intended.
In aerospace, where quality control is even more stringent, 3D scanning helps guarantee that engine parts, wings, and other components are safe and reliable.
This accuracy translates to higher-quality products, less waste, and shorter development cycles, which ultimately benefits both manufacturers and consumers.
Why It Matters
Using 3D scanning in manufacturing and quality control brings significant advantages: fewer production errors, streamlined quality assurance, and faster turnaround times.
When you incorporate 3D scanning, you’re boosting the overall quality of your products, which builds trust with customers and strengthens your reputation in competitive markets.
Cultural Heritage Preservation & Restoration
3D scanning isn’t just for cutting-edge industries; it’s also transforming how we preserve and restore cultural heritage.
Museums, historians, and archaeologists increasingly rely on 3D scanning to capture artifacts, sculptures, and even entire historical sites with stunning detail. When you use 3D scanning to document historical artifacts, you create a permanent, accurate digital record that can be studied and shared globally.
In preservation and restoration, 3D scanning enables you to create exact replicas of ancient or damaged artifacts. For instance, if a historical statue suffers damage, 3D scanning can help you recreate the missing parts based on detailed digital models.
One of our customers even utilized this technology to digitally capture the entire hull of a Stapley ski race boat during its restoration, showcasing the versatility of 3D scanning in preserving intricate designs and structures.
This capability ensures that restoration efforts are as faithful to the original as possible, preserving authenticity and cultural significance.
Noteworthy Examples
One well-known example of 3D scanning in heritage preservation is the digital reconstruction of ancient ruins and monuments. Some historical sites, like temples or statues, have endured extensive wear over centuries.
By capturing these structures with 3D scanning, preservationists can digitally restore them, giving future generations a view of what they once looked like. Museums also benefit by creating 3D-printed replicas, allowing visitors to interact with historically significant pieces without risking damage to the originals.
Why It Matters
3D scanning makes cultural heritage more accessible and sustainable. With detailed digital models, you’re helping preserve history in ways that were previously unimaginable.
This technology also allows scholars and enthusiasts to study artifacts closely, even if they’re halfway around the world, opening up new opportunities for education and appreciation of history.
Healthcare & Biomedical Engineering
In healthcare, the applications of 3D scanning are life-changing. This technology allows you to create highly personalized medical solutions that range from prosthetics and implants to complex surgical models.
By capturing a patient’s unique anatomy with 3D scanning, you can develop custom-fit medical devices that enhance comfort, functionality, and overall patient satisfaction.
Patient-Centric Applications
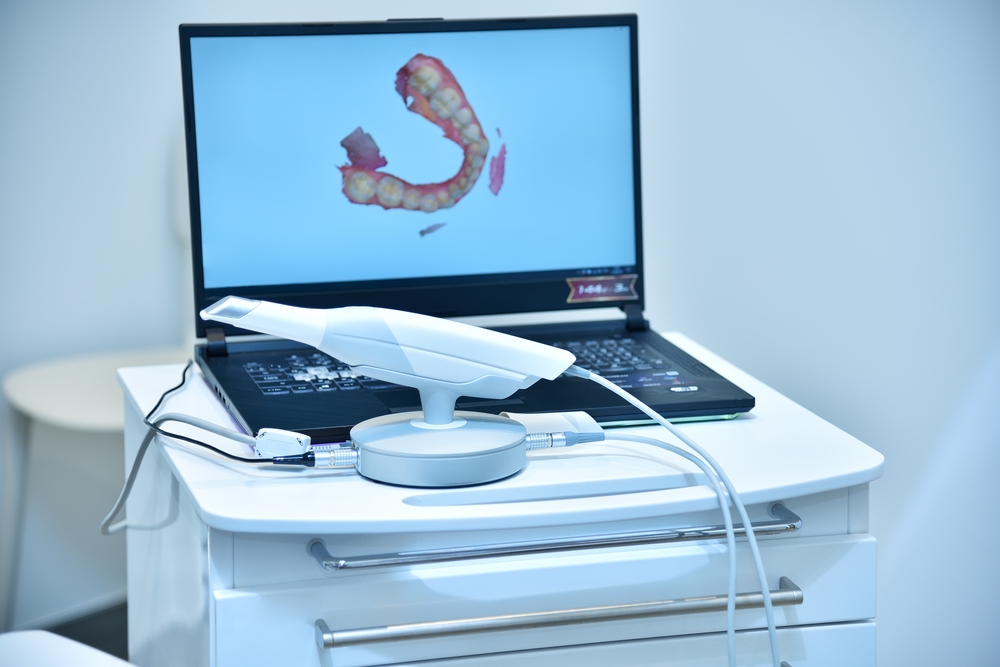
3D scanning is especially valuable in dental, orthopedic, and reconstructive surgeries, where precision is paramount. For example, dentists use 3D scanning to design perfectly fitted dental crowns, while orthopedic surgeons rely on it to model and produce custom implants.
In complex surgeries, 3D-printed organs or body parts allow surgeons to practice on accurate models of the patient’s anatomy, which can significantly increase the success rate of challenging procedures.
Real-World Examples
Consider how 3D scanning assists in creating prosthetics tailored to each individual. Instead of a one-size-fits-all approach, 3D scanning allows you to match the prosthetic precisely to a person’s measurements and needs, leading to better mobility and comfort.
Another example is the use of 3D scanning to produce custom-made hearing aids that fit perfectly, providing greater sound quality and comfort for the wearer.
Why It Matters
By incorporating 3D scanning, you can offer patients tailored solutions that enhance their quality of life.
Healthcare providers benefit, too, as 3D scanning streamlines the design process and reduces the time and costs associated with traditional manufacturing methods.
This technology is pushing the boundaries of personalized medicine and transforming patient care.
Reverse Engineering
Reverse engineering has become a cornerstone of modern innovation, and 3D scanning technology plays a pivotal role in this process. Whether you’re recreating legacy parts, improving existing designs, or analyzing competitor products, 3D scanning gives you the tools to easily capture precise, high-resolution data.
Accelerating Product Development
With 3D scanning, you can analyze an object’s geometry in detail and create accurate digital models that serve as the foundation for design modifications or reproduction. This is particularly valuable when you’re dealing with older products where original CAD models no longer exist.
By scanning the physical object, you can reconstruct a digital version that allows for refinement or seamless integration into new systems.
Enhancing Design Capabilities
When reverse engineering products, 3D scanning eliminates the guesswork. It allows you to dissect and study existing designs down to the smallest details, enabling you to understand their functionality and improve upon them.
For example, in the automotive or aerospace industries, you can scan worn-out components to recreate exact replicas or upgrade the designs for better performance.
Real-World Applications
Take the example of manufacturing replacement parts for discontinued machinery. With 3D scanning for reverse engineering, you can quickly digitize the existing part, analyze its dimensions, and produce an exact match.
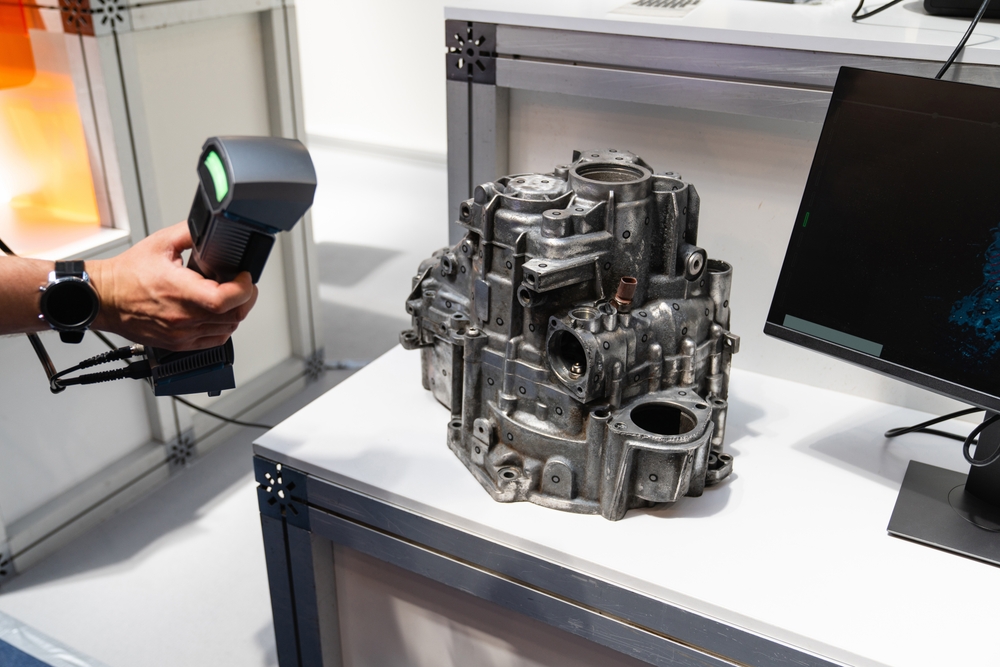

Similarly, engineers can study the design of competitor products by creating a detailed model that reveals hidden intricacies and potential areas for innovation. This approach accelerates prototyping, helping you bring products to market faster.
Why It Matters
3D scanning simplifies reverse engineering by making it more accurate, efficient, and accessible. It allows you to bridge the gap between physical and digital worlds, ensuring that even the most complex designs can be analyzed and reproduced without error.
By leveraging 3D scanning for reverse engineering, you’re reducing development costs, saving time, and opening the door to more innovative product designs that meet the demands of modern industries.
Conclusion
In each of these fields, the applications of 3D scanning are not just transforming the way work is done; they’re also driving new possibilities.
From boosting precision in manufacturing and healthcare to preserving the world’s cultural heritage and building smarter infrastructure, 3D scanning has proven invaluable.
As this technology advances, the potential for 3D scanning applications will only grow, pushing industries further and inspiring innovative solutions to complex challenges.
Embracing 3D scanning is about more than adopting new tools; it’s about embracing the future of possibility. Explore our range of handheld and desktop 3D scanners to find the perfect solution for your projects and take your innovation to the next level.

![Top 4 Applications of 3D Scanning [Explained in Detail] Top 4 Applications of 3D Scanning [Explained in Detail]](https://cdn11.bigcommerce.com/s-y1xcm/images/stencil/1000x1000/uploaded_images/shutterstock-1420444052.jpg?t=1732100882)